What is Pellet Fuel?
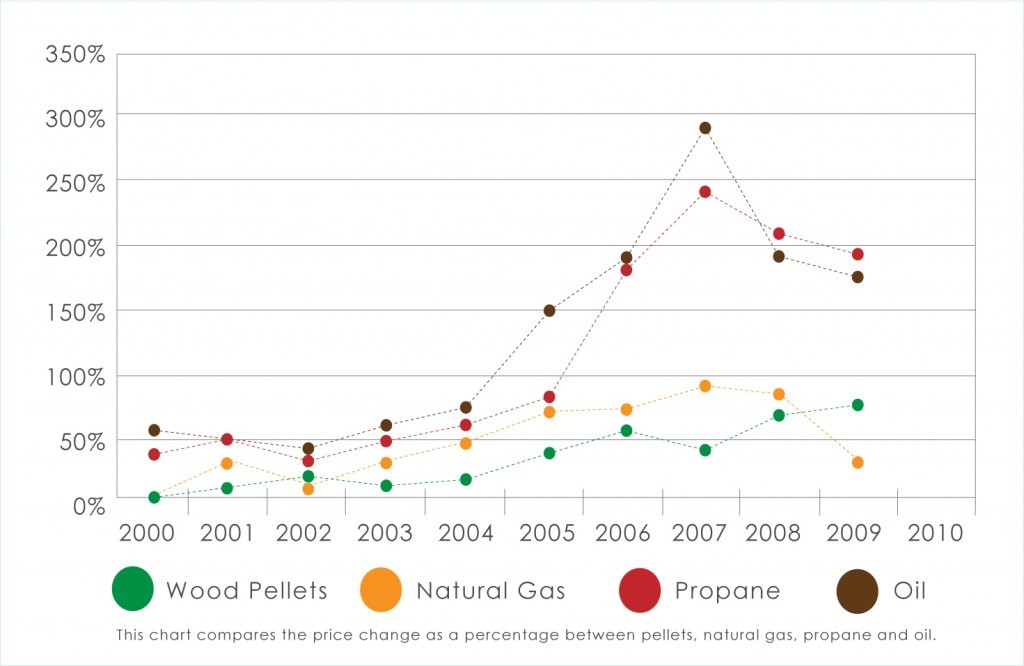
Declared CO2 neutral by the EPA, pellet fuel is simply a less expensive, more environmental home heating alternative to other fuels. In fact, the price of wood pellets has remained virtually unchanged over the last ten years. Join in today and help us divert millions of tons of waste from landfills and turn it into usable energy.
Environmental Benefits
Sustainability
Pellet fuel manufacturers use left over saw dust and excess pallets as the raw materials for wood pellets. This makes pellet fuel a biomass product. A biomass product is a renewable energy source derived from living, or recently living organisms such as wood, waste, and alcohol fuels. Wood pellets are also allergy-free.
Efficiency
Pellets have 5-10% moisture content in comparison to 30-60% moisture content typically found in cordwood and woodchips. Moisture needs to be burned off before the fuel begins to burn. So, low moisture content means higher energy content, comparable to that of a high caliber coal.
Wood pellets have a higher BTU content than cordwood. In fact, most wood pellets maintain a BTU output of 350,000 per cub. feet of fuel versus 70,000 to 90,000 for cordwood. A higher BTU translates to more heat.
Reducing CO2 Emissions
Pellet fuel burns cleaner than any other solid fuel.
Carbon emissions saved per household by burning on average 2.67 tons of pellet fuel:
-If you heat with electricity you will save 8872 lbs.
-If you heat with oil you will save 2518 lbs.
-If you heat with LPG you will save 1893 lbs.
-If you heat with natural gas you will save 1466 lbs.
If every household in the United States used wood pellet fuel for heating, the total carbon emissions of the United States would drop by more than 8%.
Data taken from Dr. Jerry Whitfield’s talk “Reduction in Greenhouse Gases Using Biomass Pellets for Residential Space Heating”, 6/3/98